

- Say No
Wild Caught
Region:
QLD
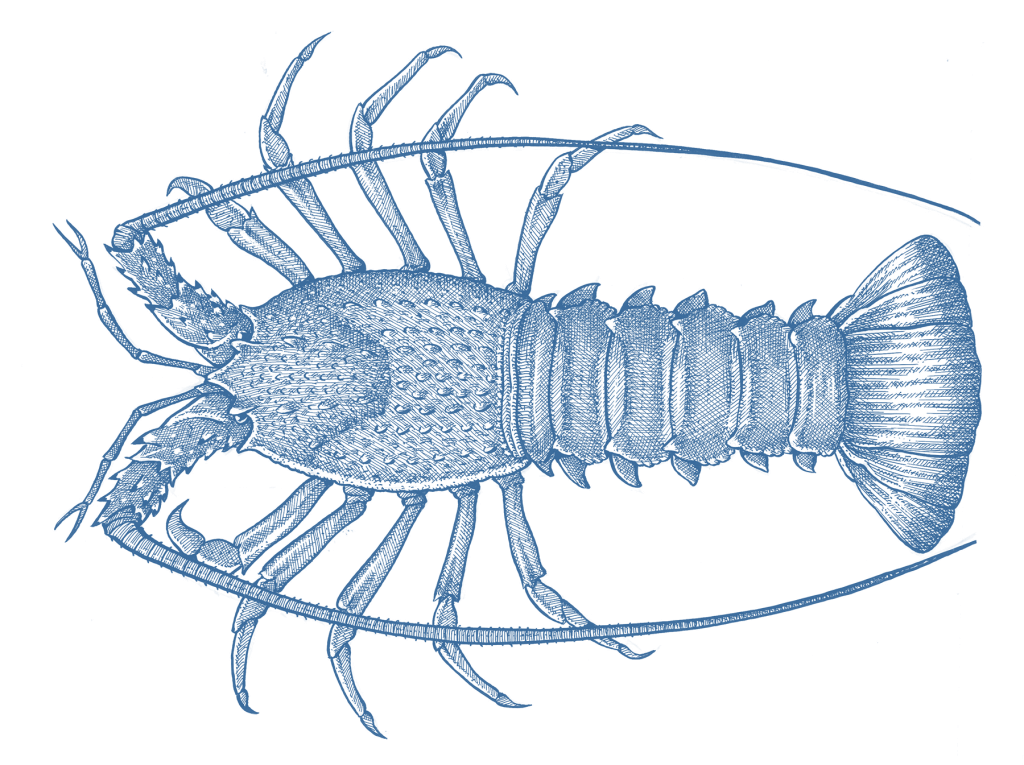
- The term ‘Balmain bugs’ refers to four species of fan lobster that occur along the eastern coastline of Australia, which are managed as though they were a single species. Although there is a lack of stock status information, there are no immediate concerns over the stock status of these species.
- Balmain bugs are caught in trawl fisheries mainly fishing for prawns and scallops.
- The accidental catch of threatened and endangered species like endemic sharks and rays is a major issue in Australian prawn fisheries. The Queensland government abandoned an independent observer program in 2012 so bycatch reporting is not reliable and science-based management is hampered as a result.
- Balmain bug catch is associated with that of a seriously overfished species, saucer scallop.
- Balmain bugs are caught using otter trawls that operate just above the seafloor. Some areas of seafloor are protected in area closures and marine parks but the fishery operates largely outside QLD marine parks.
- QLD: East Coast Trawl Fishery: (71t in 2020, 64t in 2019)
The term ‘Balmain bugs’ refers to four species of fan lobster that occur along the eastern coastline of Australia. Balmain bugs are caught in trawl fisheries in NSW and QLD, with the majority caught in QLD. The same stock is caught in both states, but managed as separate units. The health of the QLD balmain bug fishery is poorly understood, and while there are not serious concerns about overfishing, the species is conferred relatively little protection from fishing from marine parks in QLD, as it is largely caught beyond their bounds.
In QLD, Balmain bugs are caught as a byproduct in a trawl fishery that targets multiple species of prawns and scallops. The fishery operates within and around the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park.
This fishery has a high level of discards and it is concerning they are not required to be reported. The most recently available data estimated 25,271t of discards in 2014, compared to 6702t of retained catch in the same year. Balmain bug catch is associated with fishing targeting a seriously overfished species, the saucer scallop.
New evidence has shown that the Queensland stock of saucer scallops is at 15% of historic levels, meaning it is overfished. Queensland fishery rules state that a fishery should be closed when a stock is below 20%, and yet one area of this fishery off Fraser Island and the southern Great Barrier Reef remains open. Even low levels of scallop bycatch associated with fishing for balmain bugs would negatively impact the recovery of the stock.
Independent fishery observer programs are an important method of verifying protected species interactions, as well as other fishery impacts, such as the type and volume of discarded catch. Unfortunately the QLD Government has closed the observer program for all QLD managed fisheries in 2012. In the intervening six years, there has been no independent on-vessel monitoring of the impact of the fishery, which is unacceptable for fisheries operating in the ecologically sensitive regions of the Great Barrier Reef. Concerns have been raised regarding under-reporting of endangered species caught in the fishery in logbooks. Since there is no record of actual protected species interactions over time, the ecological impacts of this fishery cannot be measured or managed.
The fishery will be required to resume an independent observer program by 2024, likely to be based on e-monitoring. While it is welcome, the program should be implemented sooner. This and other reforms currently underway in the Queensland fishery have strong potential to improve the GoodFish ranking of this seafood option if implemented quickly and effectively.